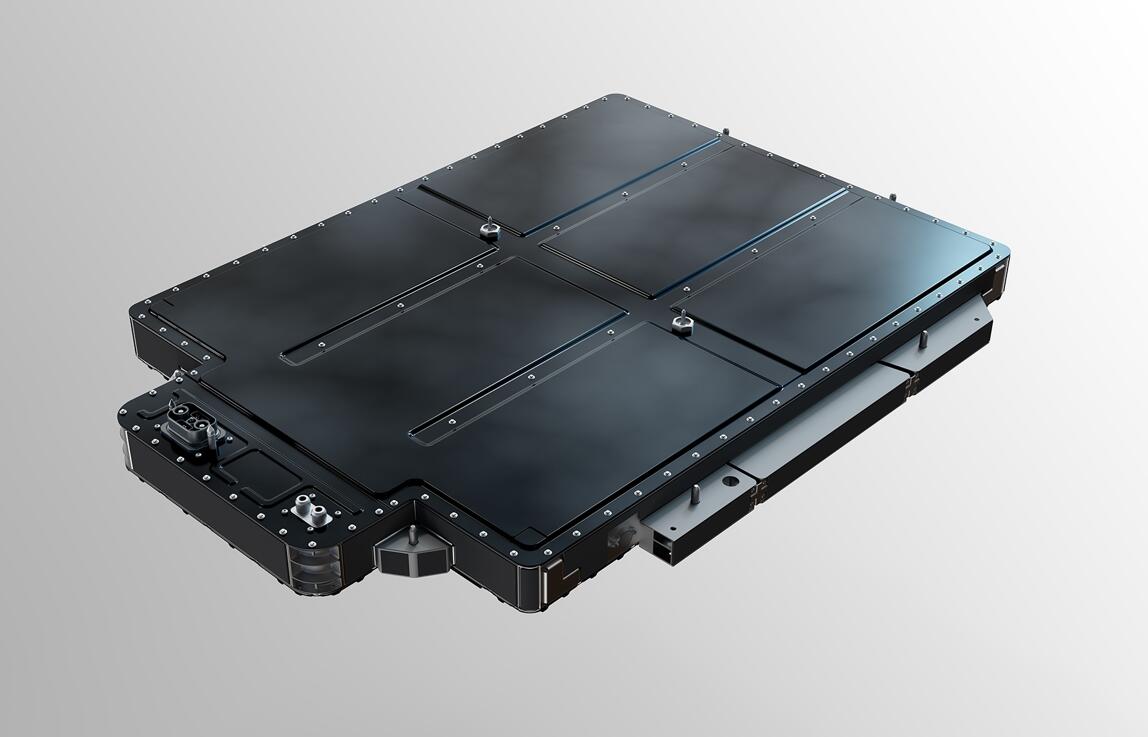
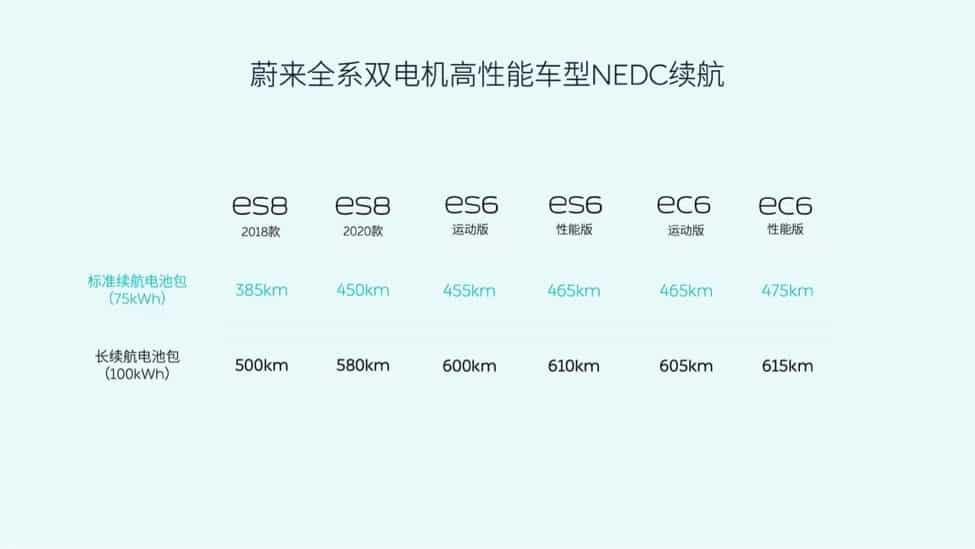
Models equipped with the new 75 kWh battery are now available for orders, and will be delivered to users from this November. Prices are the same as models with the previous 70-kWh pack.
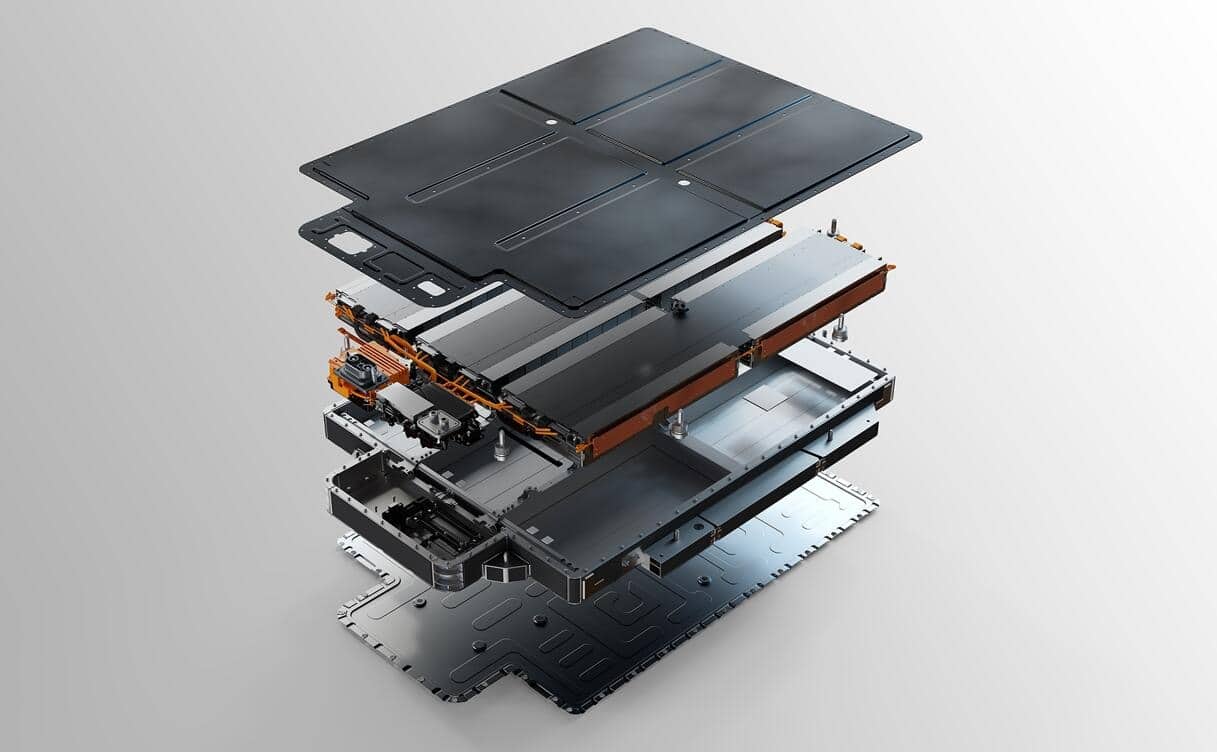

After previous rumors, Nio has confirmed the launch of a 75-kWh hybrid battery pack to replace the previous 70-kWh version, which is expected to bring customers a longer range while reducing costs.
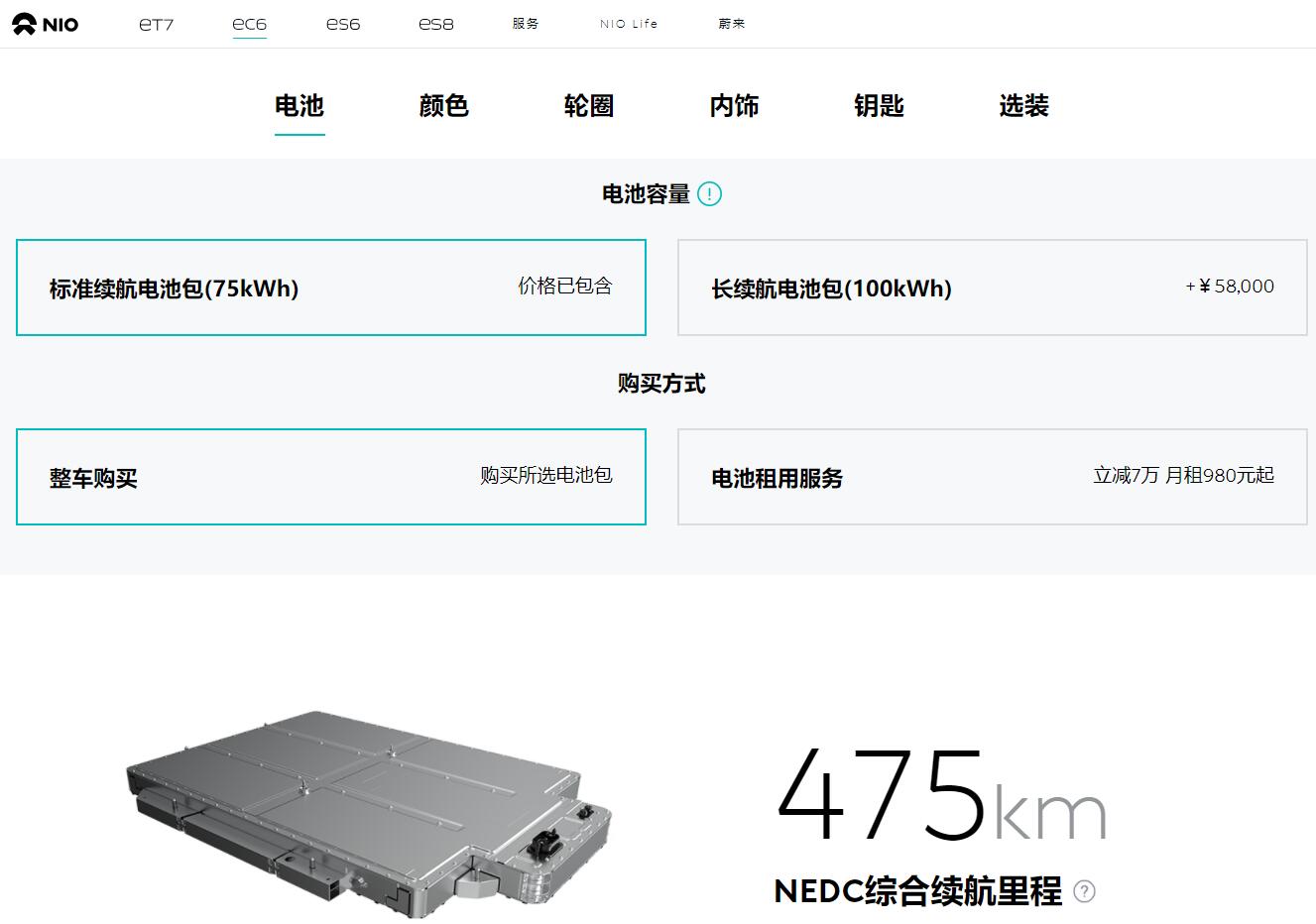
The electric car company officially announced Thursday the launch of the 75-kWh standard range version of the hybrid pack, with orders for models equipped with the pack being taken immediately and their deliveries set to begin in November.
A check of Nio's website by CnEVPost shows that the company's currently available models, the ES8, ES6 and EC6, all offer a choice of 75-kWh and 100-kWh packs, meaning Nio is phasing out its previous 70-kWh version with the 75-kWh pack.
Although deliveries of models with this new battery pack will not begin until November, there is no need for consumers to delay their vehicle purchase plans.
Unlike other car companies that cause consumers to wait for new models when they launch upgraded versions, Nio consumers can choose to use this battery when it becomes available because their vehicle's battery can be replaced at any time.
Nio said that starting today, both the 75-kWh pack and the long-range 100-kWh lithium-ion battery pack will be available for new Nio vehicle orders. Prices of models with the 75-kWh pack and the battery rental program BaaS (battery as a service) are the same as the previous 70-kWh pack.
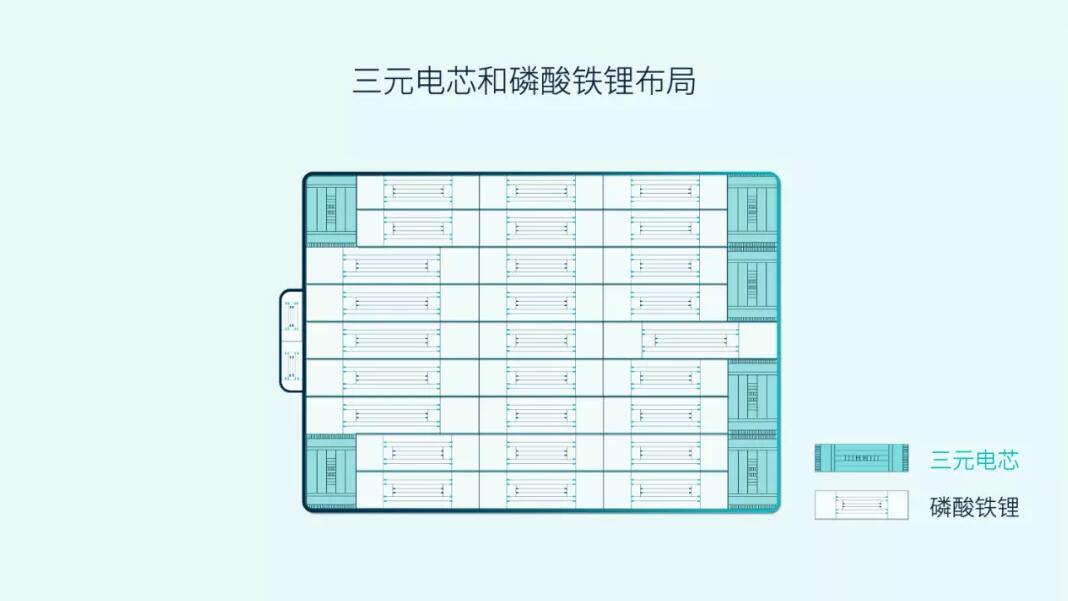
The 75-kWh pack is a hybrid of the common ternary lithium battery cells and lithium iron phosphate (LFP) cells, making Nio the world's first electric vehicle company to use both materials in its packs.
It offers the same performance as ternary lithium batteries with a longer winter range and accurate state of charge (SoC) estimates supported by Nio's patented technologies, the company said.
Nio said it has designed complete thermal management software and hardware systems for the new pack, which allows it to reduce mileage loss in cold temperatures by 25 percent compared to its LFP counterpart.
Here is a description of some of the technical details provided by Nio:
The comprehensive environment shielder applies low-thermal conductivity materials and innovative structural design for the source of heat loss in extremely cold environments in order to effectively improve passive thermal insulation performance.
The intelligent thermal system coupling battery heat generation dynamically adjusts thermal control targets in combination with battery heat to balance the drive experience and energy consumption.
The radiant thermal compensation heater uniformly heats the battery cells to maintain the working temperature of the battery while taking into account the energy consumption. The hybrid layout of ternary lithium cells and LFP cells makes full use of the low-temp performance advantage of ternary lithium cells to improve the overall battery performance in low temperatures.
And the dual chemistry control algorithm precisely controls the performance of ternary lithium and LFP cells in cold temperature to improve the low-temp energy efficiency of the whole battery system.
The current mainstream battery pack includes ternary lithium batteries, as well as LFP batteries. all models previously offered by Nio used ternary lithium batteries from the power battery giant CATL.
The advantages of ternary lithium batteries are high energy density and good performance, but the shortcomings are lower safety, poor cycle life, and high cost.
LFP batteries cost lower and have higher cycle life, higher safety, but the energy density is lower and the low-temperature performance is poor.
Using both materials in a battery pack is expected to reduce the cost of Nio batteries, but the challenge is to estimate the range of this hybrid battery.
Nio appears to have previously been preparing for this and has filed a patent for a new battery system SoC estimation method in April 2021.
The company has integrated a combined battery module consisting of LFP cells and ternary (NCM) cells in a series connection to form a dual-system battery system.
Nio said Thursday that its in-house-developed SoC estimation system integrates innovations in software algorithms and hardware applications to reduce estimation errors to less than 3 percent, achieving the level for ternary lithium batteries.
"The dual chemistry SoC algorithm fully takes advantage of ternary lithium and LFP battery systems to realize constant battery SoC estimation and guarantee the accuracy. A high-power DCDC within the battery ensures fast, real-time and balanced SoC calibration," Nio said.
In addition to these, the 75-kWh pack uses next-generation cell-to-pack (CTP) technology that simplifies manufacturing and assembly by 10 percent, increases volume utilization by 5 percent, and boosts energy density by 14 percent to 142 Wh/kg, according to the company.
(Photo source: Nio)