BYD Semiconductor announced on Aug. 5 that it has shipped LED displays for unmanned vehicle manufacturer Neolix, marking the company's entry into this new field.
The Neolix L4 low-speed unmanned vehicle has a BYD Semiconductor-developed LED display at the front and one at the rear of the vehicle.
BYD Semiconductor says the displays are automotive-grade, modular, common-cathode drive displays. The common cathode drive design reduces energy consumption by about 30 percent compared to other products and reduces the temperature of the screen by about 20°C.
The display enables wireless remote cluster control via CAN bus, including status alerts for vehicle steering and braking, and also supports scrolling text and motion graphics and automatic brightness adjustment.
BYD Semiconductor says it will cooperate with well-known manufacturers in the fields of artificial intelligence and autonomous driving.
BYD Semiconductor was established in October 2004 and entered the industrial MCU field in 2007, ranking first in China in terms of market share for industrial-grade touch MCUs.
BYD Semiconductor's business then extended across from industrial-grade MCUs to automotive MCUs, and launched the first generation of 8-bit automotive MCUs in 2018 and the first generation of 32-bit automotive MCUs in 2019, with batch loading in BYD's full range of models.
On June 30, BYD announced that the application to spin-off BYD Semiconductor to ChiNext, a NASDAQ-style subsidiary of the Shenzhen Stock Exchange for listing was accepted by the Shenzhen Stock Exchange.
From 2018-2020, BYD Semiconductor's net profit attributable to shareholders of the parent company was RMB 33 million ($5.11), RMB 30 million and RMB 32 million, respectively.
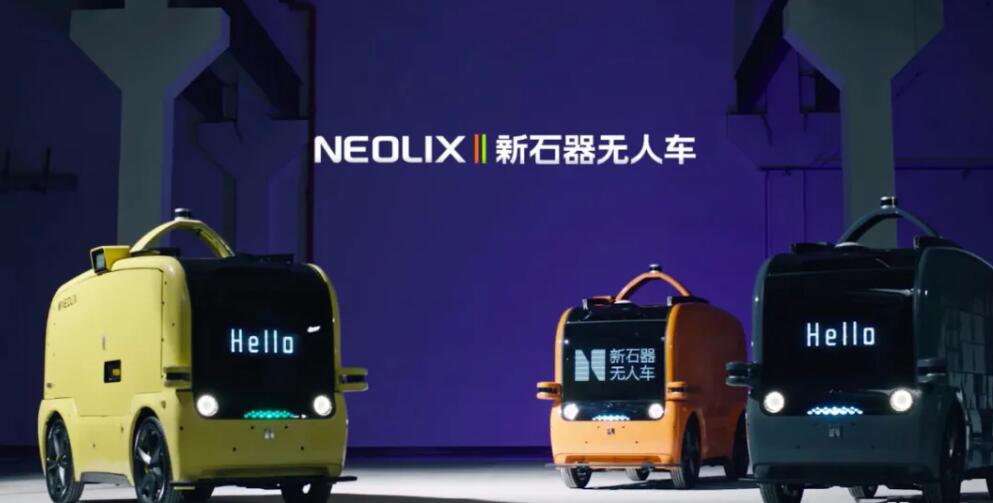

(Photo source: BYD Semiconductor)