(Photo source: CnEVPost)
Nio delivered 7,931 vehicles in July 2021, up 124.48% year-on-year, down 2% month-on-month.
- We estimate Nio's 2022 revenue to show the value of the stock.
- The methodology includes a car sales forecast and average selling prices.
- Our evaluation indicates that the stock is currently fairly priced.
- None of the currently acute regulatory risks apply to Nio.
Introduction
Nio, China's arguably most successful EV startup, saw an incredible performance both business-wise and in the capital market. More investors have joined the camp of those bullish about the electric car maker's prospects.
In 2021, Nio has been solidifying a high premium profile in China, launching a new model, the ET7. Nio has also recently started shipping the ES8 to Norway, with global expansion ambitions.
This article follows an approach similar to that we used in our latest Xpeng analysis, estimating the value of the stock based on its projected future sales performance.
Revenue estimation
In this section, we will project Nio's revenue by 2030 and use the 2022 figure to evaluate the stock's current investment potential. The revenue will be calculated by multiplying projected car deliveries with average selling prices.
The calculation of whole fleet (including ES6, EC6, ES8 and ET7) sales is based on a top-down methodology. It starts with a forecast of light vehicle sales in China.
According to CAAM, China's light-vehicle sales will hit 22.2 million in 2021. Under an assumption of slowing economic growth affecting the auto market, we estimate the growth rate will decline to 4% gradually. The market will reach 32.6 million in 2030.
Speaking of the market share, we assume Nio can reach 2.4% of the total market by 2030. It results from the fact that William Li, the founder of Nio, has aligned the company's goals with those of iconic brands like Mercedes Benz, BMW and Audi.
We linearized that number and estimated Nio's 2022 market share and deliveries, which will account for 0.6% and 152,066 units, respectively.
To calculate the revenue, we also need to project the average selling price (ASP). Historically, Nio's ASP has been declining as new models have been rolled out.
This trend will continue, whereas we think the ASP will remain higher than CNY 300,00 per vehicle. We set a declining rate for ASP calculation, from -2% in 2021 to -0.5% in 2030. The ASP in 2022 will be CNY 328,000.
Per this projection, Nio's 2022 vehicle sales will be CNY 50 billion. Apart from car sales, Nio also generates revenue from selling charging facilities and related services, data, insurance and merchandise.
These segments have correlated to vehicle sales and shown a faster growth pace. Thus, we project a slightly increasing percentage of revenue from selling them. In 2020, the number was 6%, and we allocated 7% and 9% for 2022 and 2030, respectively.
In total, Nio is expected to make CNY 53.5 billion (USD 8 billion) in revenue in 2022. Similar to our Xpeng analysis, we multiplied Nio's PS ratio in 2022 by nine (referring to the Street's average expectations). Its fair market capitalization target is thereby around USD 74 billion.
Risks
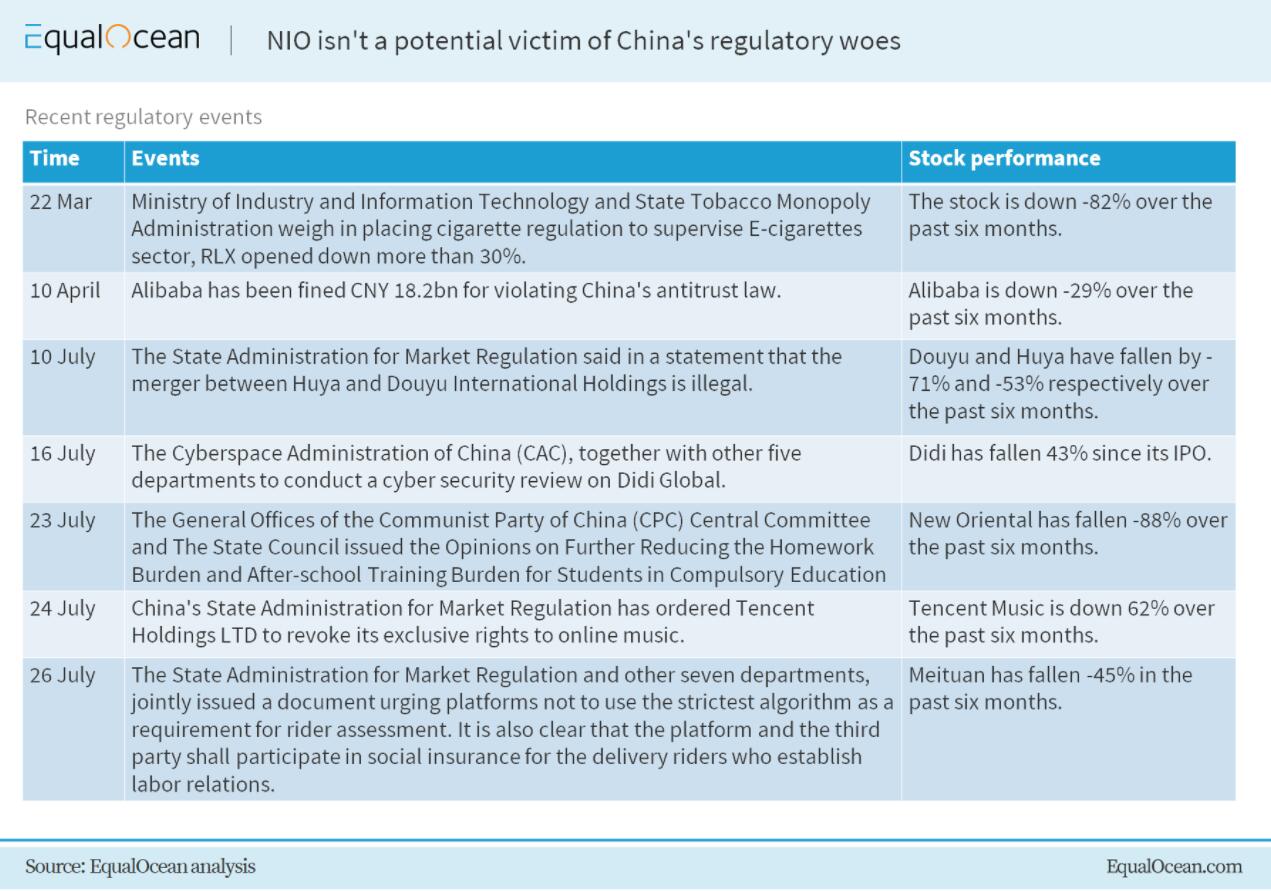
Nio has recently been indirectly involved in the regulatory crackdown-related narrative. We think investors' massive selling may insignificantly hurt the company's business. To specify all the possible risks, we summarize all the incidents concerning Chinese concept stocks within this year.
The antitrust and other new regulations are the key obstacle imposed by the central government. Some famous 'victim' cases include Tencent Music's copyrights, Alibaba's 'pick one from two' strategy and Meituan's rider employment and other issues. Obviously, the NEV market in China is still in its infancy (compared with ICE cars). Nio is certainly not a monopoly.
Data/cybersecurity concerns are also not suitable for Nio. In early July 2021, it was reported that Didi Global had illegally collected users' personal data. Clearly, the ride-hailing giant possesses huge chunks of users' travel information.
However, Nio is also collecting data that seems less significant than important route data handled by legitimate third-party providers like map products of Baidu and the likes of AutoNavi.
Nio and its peers won't see anything like what happened to the country's edtech industry either: the central government, which is ''seeking to decrease workloads for students and overhaul a sector that has been 'hijacked by capital,'" is rather interested in the nationwide EV adoption.
In short, Nio, much like any local EV maker, is not exposed to these major risks.
Apart from regulatory risk, supply chain issues are worth discussing. The issues seem to remain controllable, but investors need to keep eyes on them – the component shortage will be a hot topic in the upcoming Q2 earnings calls.
Conclusion
Among Chinese concept stocks, Nio is a company with a solid product line, growing sales and great prospects. The stock has gone down and has remained volatile since the beginning of 2021. Suffering from the chip shortage, it is currently fairly priced. And is well set to gain more in the following quarters.
This article was first published by Niko Yang and Ivan Platonov on EqualOcean, an investment research firm focusing on China.