Tesla's current Chinese battery supplier is CATL, but it appears the company may be adding a new one.
In an effort to increase its sourcing of low-cost batteries, Tesla is in talks with EVE Energy about including it in its supply chain for its Shanghai plant, Reuters reported Friday.
The talks are advanced and the two are looking to finalize the partnership in the third quarter, the report said, adding that EVE Energy is in some of the final stages of testing for Tesla's products.
EVE Energy primarily produces lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries, which are cheaper to produce because they use iron instead of the more expensive nickel and cobalt. But LFP batteries typically offer shorter charge times than the more popular nickel-cobalt batteries.
If negotiations are successful, EVE Energy will become Tesla's second LFP battery supplier, after CATL.
EVE Energy is a much smaller player than CATL, a giant with half of China's power battery market share.
In April 2021, China's power battery installed base was 8.4 GWh, down about 7 percent from March and up 134 percent year-on-year, data released Wednesday by the China Automotive Battery Innovation Alliance showed.
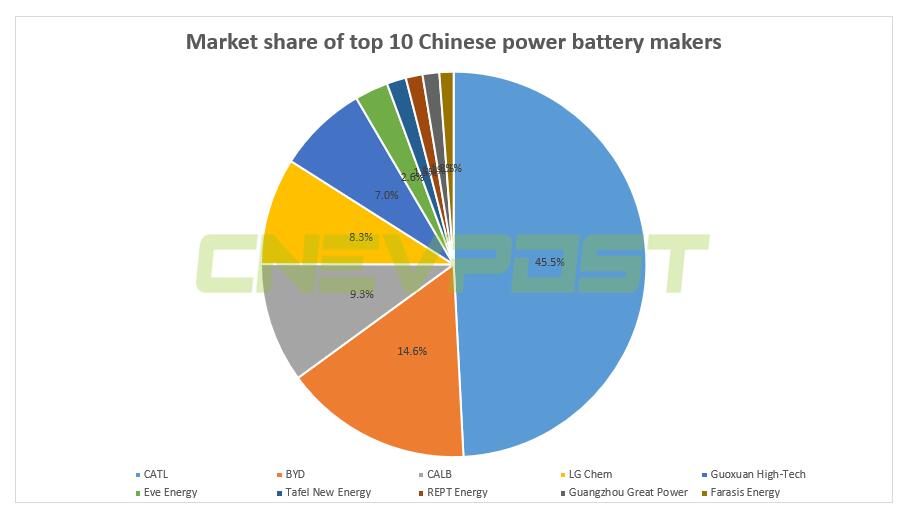
In April, the top 10 power cell companies had a total installed base of 7.8 GWh, with a combined market share of more than 90 percent.
CATL remained in the first place, with 3.82 GWh installed in April and a 45.5% market share.
Notably, this is the first time CATL's market share has fallen below 50% this year, a new low since July last year.
EVE Energy's power cell installed base in April was 0.22 GWh, with a 2.6% market share. from January to April, the company's power cell installed base was 0.61 GWh, with a 1.9% market share.
If Tesla takes EVE Energy into its supply chain, the latter's market share in China is expected to soar.
(Graphic by CnEVPost)