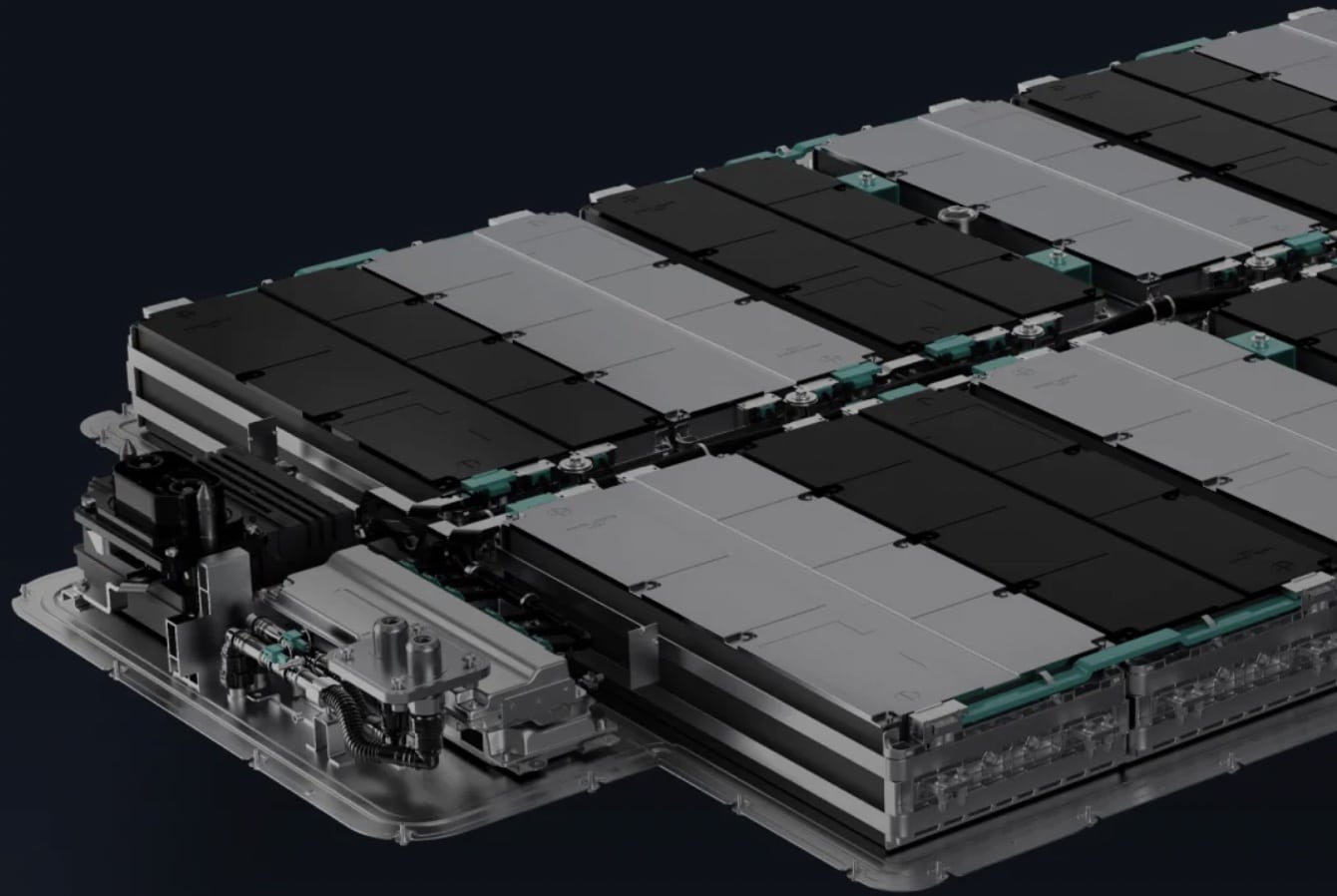
Nio today unveiled a 150kWh solid-state battery at Nio Day in Chengdu, giving the entire Nio product lineup on sale an NEDC range of more than 850km, and its first sedan, the Nio ET7, an NEDC range of more than 1000km.
The 150kWh battery uses industry-leading mass-produced solid-state battery technology to achieve a 50% increase in energy density.
The solid-state battery uses a solid-liquid electrolyte to ensure the safety of the cells. Through innovations in materials and processes, a super high energy density of 360Wh/kg has been achieved.
The 2018 ES8's NEDC range with the 150kWh battery is over 730km, and the new ES8 NEDC range is over 850km.
The performance versions of ES6 and EC6 have an NEDC range of over 900km, and the Nio ET7 has an NEDC range of over 1,000km with the 150kWh battery.
Nio plans to start delivering 150kWh battery pack in the fourth quarter of 2022, and will provide customers with flexible battery upgrades to allow them to continue to enjoy the development of technological advances through battery swap technology.
Nio has not disclosed the partner that will manufacture the battery, but yesterday 36kr reported that a potential partner is Jiangsu Kunshan's ChingTao, and this information was confirmed by insiders at ChingTao.
Compared to traditional lithium batteries, solid-state batteries are considered to be the ideal battery technology for electric vehicles. It offers significant improvements in energy density, charging efficiency and safety, and represents a new technological breakthrough for the industry.
Traditional lithium batteries use liquid electrolytes, which have disadvantages such as low charging efficiency and poor thermal stability. More importantly, the energy density of liquid lithium batteries is slow to increase, and its energy density limit is considered to be only 300Wh/kg, which limits the range improvement of electric vehicles.
However, solid-state batteries can easily break through this upper limit and reach 400-500Wh/kg, and also solve the problems of poor stability and low charging efficiency.